池俣吉人研究室

受動歩行ロボットは、重力のみによって緩やかな下り坂を歩くことができます。エネルギー効率が高く、ヒトの歩行に近いです。
本研究室では、受動歩行原理に基づいた歩行ロボットを開発しています。また、受動歩行原理からヒト歩行のメカニズムを解析しています。最近では、3Dプリンタなどを用いて、ロボットの部品を作成しています。ものづくりの好きな学生さんは、是非本研究室へ話を聞きに来て下さい。
| 教員名・所属 | 池俣吉人 / 総合理工学科 機械・航空宇宙コース |
|---|---|
| 専門分野 | ロボット工学 |
| 研究テーマ |
|
| 研究キーワード | 歩行ロボット、受動歩行、歩行原理、平衡点解析、歩行支援機 |
| 教員紹介URL | https://www3.med.teikyo-u.ac.jp/profile/ja.10340e4e9df7cf76.html |

受動歩行原理に基づいた歩行ロボットの開発
ヒューマノイドに代表される歩行ロボットは、最先端テクノロジーの結晶です。その要となっているのが、ZMP(Zero Moment Point)であり、転倒しないように歩かせたりするのに強力なツールです。しかしながら、ZMP規範の制御方法では、高いエネルギー効率を実現することは困難であり、その歩行は自然さに欠けます。一方、受動歩行は、T.McGeerによって1990年に提唱され、歩行機のもつダイナミクスと環境(ここでは、スロープ)との相互作用のみによって、理想とする自然な歩容を形成します。本研究では、受動歩行原理に基づくことで、自然かつ高効率な歩行ロボットを開発します。

受動歩行原理に基づいた歩行支援機の開発
従来の歩行支援機では、モータ駆動による安全性の低下、駆動系・制御系の搭載により重量の増加ならびにコストの増大、自然な動きを生成する難しさ等の問題があり、広く利用されるまでには至っていません。本研究では、受動歩行原理に従うことにより、これらの問題を解決して、安心・安全・安価な歩行支援機を開発します。歩行支援機の有効性は、ヒトに装着して検証するだけでなく、受動歩行ロボットに装着して検証します。もし有効であれば、ロボットは水平面もしく極低スロープを歩くことができます。他には見られない検証方法であり、定量的評価を行うことができます。
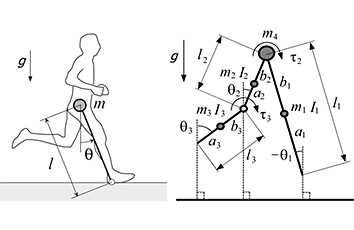
ヒト走行原理の解明および走行支援機の開発
ヒトは「受動走行」のような力学現象を巧く利用して走っており、その原理は複雑なものでなく、力学的観点から明快に説明できるものと考えられます。本プロジェクトでは、受動走行の研究で培った知識および経験から、ヒト走行の簡易モデルを構築します。同モデル(離散モデル)の解析から、a)走行の周期運動の生成、(b)走行の周期運動の安定化、の原理を明らかにします。さらに、連続モデル(運動方程式)を用いて、c)接地期の脚運動、(d)滞空期の脚運動、の原理を明らかにします。また、ヒト走行の解析で得られた知見に基づいて走行支援機を開発します。同支援機により、より楽に、より速く走れるようになると考えられます。
2014年度
| 演題名 | 学会名 | 研究室 | 内容 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 簡単なリムレスホイールによる3次元運動の実現 Realization of 3D Motion of a Simple Rimless Wheel | ロボティクス・メカトロニクス講演会 | 池俣吉人研究室 | 詳細 |
| ヒトの2脚歩行メカニズムの仮説と2脚受動歩行による仮説検証 Hypothesis of 3D Human Walking, and Verification of the Hypothesis by 3D Passive Walking | 計測自動制御学会 システムインテグレーション部門 講演会 | 池俣吉人研究室 | 詳細 |
2015年度
| 演題名 | 学会名 | 研究室 | 内容 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Dリムレスホイールの実験的研究 An Experimental Study for 3D Rimless Wheel | ロボティクス・メカトロニクス講演会 | 池俣吉人研究室 | 詳細 |
| 平地歩行における移動効率の理論限界 | 計測自動制御学会 システムインテグレーション部門講演会 | 池俣吉人研究室 | 詳細 |
2016年度