Professor Hajime Kono of the Department Internal Medicine School of Medicine said,
The mechanism of chronic inflammation involved in the development of various diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease
We are trying to clarify this from the perspective of "danger signals," which are sensors inside the body.
We have so far elucidated the mechanism by which uric acid and cholesterol crystals act as danger signals and worsen arteriosclerosis.
The aim is to develop new treatment and prevention strategies for arteriosclerosis.
The intracellular molecules in the body
Functions as a sensor of innate immunity

Immunity is the function of protecting the body from pathogens such as bacteria and viruses, and eliminating waste products and dead cells in the body. It also works to repair damaged cells. This immunity is divided into two types: "innate immunity" that is inherent in all living things, and "acquired immunity" that memorizes a pathogen that has been infected once and prepares an antibody that works only against that pathogen (antigen). There is. Innate immunity causes an "inflammatory reaction" as the first group to respond to the invasion of pathogens and damage to cells of the body, and acquired immunity is the second group to respond when it is still unprotected.
When innate immunity detects the invasion of foreign enemies, it uses sensors such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs) that can identify the characteristic structures of bacteria and viruses. Innate immunity can detect that one's body has broken and cause a reaction even in the absence of foreign enemies. This self-generated stimulus is called the "Danger signal" and is programmed by the Danger signal to trigger an inflammatory response when the sensor is activated.
Recent studies have shown that molecules such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP), uric acid, DNA, and RNA, which are abundant in cells, act as Danger signals and cause an inflammatory reaction. All of these are molecules that exist inside the cell, and when the cell is damaged and causes "cell death," the molecule that leaks from the torn cell membrane becomes a Danger signal and is recognized by neighboring cells to cause an immune reaction.
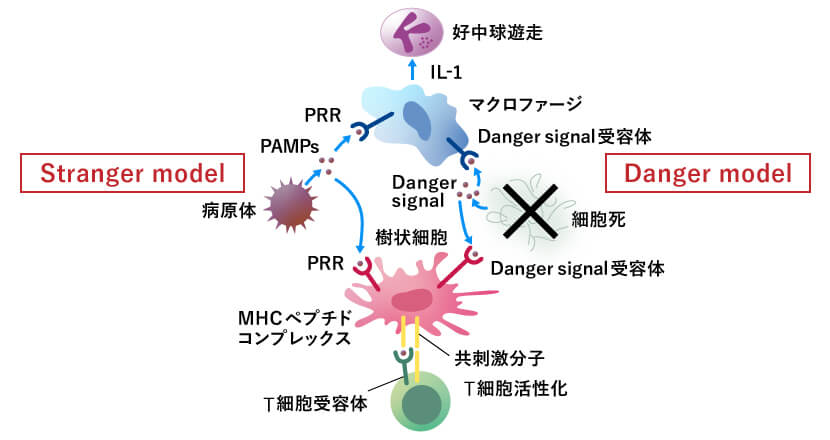
The "Danger model" (right) also emits a Danger signal as a signal to signal dead cells.

However, as human lifespans have increased, a problem has arisen. Cardiac cell death caused by arteriosclerosis and ischemia due to aging is perceived as a target for elimination, and inflammation accelerates cardiac necrosis. Professor Kono is tackling this problem, and is conducting research to elucidate the mechanisms of danger signals and chronic inflammation, which remain largely unknown.
"Natural immunity is an extremely sophisticated immune system, but the inflammatory response caused by innate immunity is a double-edged sword. We would like to find a way to control it." (Professor Kono)
Uric acid, which is a Danger signal
Affects worsening arteriosclerosis
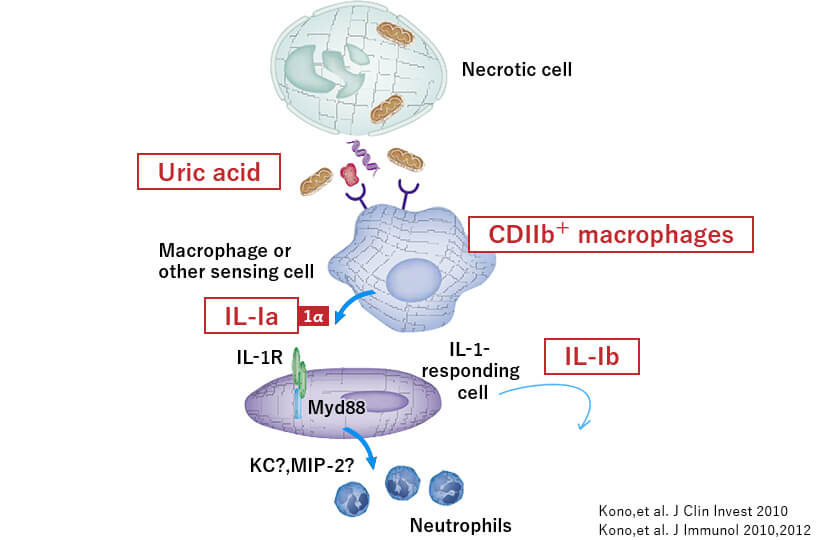
Of the danger signals within the body, Professor Kono focused on uric acid. Uric acid is a product of purine and is known to be the cause of gout. Gout occurs when uric acid levels in the blood rise, causing crystallization of urate crystals, which then enter the joints and cause intense, tingling pain like being pricked by needles from within the body. Specifically, the stimulation of urate crystals causes the production of proteins such as the inflammatory cytokine IL-1, which activates white blood cells to attack these proteins, resulting in acute inflammation.
Meanwhile, Professor Kono investigated the possibility that uncrystallized uric acid could cause inflammation. In an experiment conducted on mice with Assistant Professor Yoshitaka Kimura (Department of Microbiology, Teikyo University School School of Medicine), they found that even uric acid within the physiological concentration range acts as a danger signal for chronic inflammation and worsens the state of arteriosclerosis.
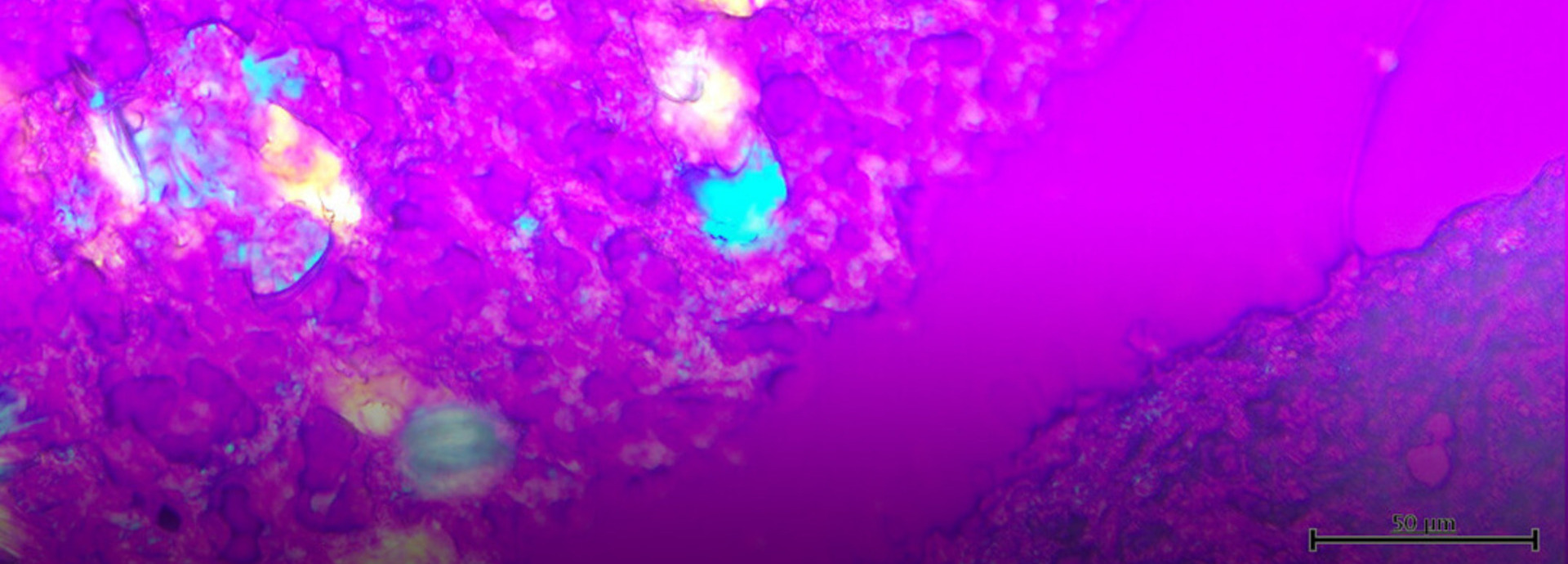
In experiments, transgenic mice with lower uric acid levels were created by introducing an enzyme that breaks down uric acid into the genes of mice with lower uric acid levels than humans. These mice were then induced to develop arteriosclerosis, and the degree of arteriosclerosis was examined. It was found that the lower the uric acid level, the less likely the arteriosclerosis to worsen. Assistant Professor Kimura also elucidated the molecular mechanism by which uncrystallized soluble uric acid promotes arteriosclerosis via AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase), an enzyme that maintains the body's energy balance. Suppressing uric acid, which acts as a danger signal, reduces inflammation, which may ultimately be effective in inhibiting the progression of arteriosclerosis.
"Mice, among mammals, have lower uric acid levels than humans and chimpanzees, but we conducted experiments by inducing arteriosclerosis in transgenic mice with even lower uric acid levels. Professor Makoto Hosoyamada (Teikyo University Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences), who is skilled in the technology of creating model mice, has genetically modified mice to create mice with uric acid levels similar to humans, and we are conducting joint research with him," says Professor Kono.
Due to cholesterol crystals
Discover the mechanism of acute inflammation
Speaking of diseases associated with chronic inflammation, allergic diseases such as asthma and autoimmune diseases such as rheumatism are known. Recently, evidence has been found one after another showing the effects of chronic inflammation due to natural immunity on diseases such as cancer, obesity, arteriosclerosis, and Alzheimer's disease, as well as on aging.
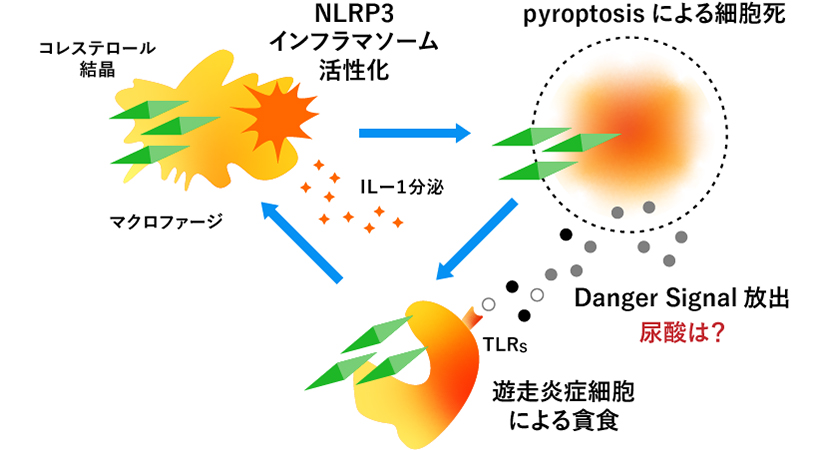
For example, arteriosclerosis is a metabolic disease in which fat components are deposited on the walls of arterial blood vessels due to excessive nutrition, and it was thought that cholesterol accumulated on the cell walls is crystallized and stabilized. As it progresses further, the arterial wall narrows and blood flow stops, leading to ischemic diseases such as cerebral infarction and myocardial infarction. In addition, when endovascular treatment such as a catheter is performed, cholesterol crystals on the arterial wall enter small peripheral arteries, causing a disease called cholesterol crystal embolism.

However, research by Professor Kono and his colleagues has revealed that arteriosclerosis is a disease in which natural inflammation plays a major role. It has been found that cholesterol crystals appear much earlier than previously thought. Acute inflammation in the arterial wall caused by stimulation by cholesterol crystals triggers a danger signal released from the damaged artery, which activates a molecular mechanism called inflammasome, a protein complex that causes inflammation, thereby worsening arteriosclerosis. They also found that mice in which inflammasomes were intentionally knocked out were less likely to develop arteriosclerosis.
"This study showed that cholesterol crystals are a danger signal, but it is also possible that uric acid is released from arteries that have undergone cell death due to acute inflammation. We believe that we need to elucidate the pathology of arteriosclerosis from both perspectives," says Professor Kono.
In both basic research and clinical
Save the patient in front of you and the patient of the future
Research into chronic inflammation and arteriosclerosis is a major challenge for Professor Kono, who works as a clinician dealing with autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This is because rheumatoid arthritis patients are particularly susceptible to the progression of arteriosclerosis and are at a high risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction. This is related not only to the effects of chronic inflammation, but also to the state of rheumatoid arthritis, and it has been shown that suppressing the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and putting it into remission also leads to the control of arteriosclerosis.
In addition, long-term administration of steroids (corticosteroids), which are standardly used in autoimmune diseases, is also one of the causes of worsening arteriosclerosis. For rheumatoid arthritis, there are effective alternatives to steroids, but for other autoimmune diseases, many have to rely on steroids, and the effects on arteriosclerosis cannot be helped.
"Patients with autoimmune diseases will have to live with the disease for decades, but even if the disease is controlled, there is a risk that the effects of chronic inflammation and steroids may worsen arteriosclerosis. As a clinician, it is necessary to look at the patient holistically, rather than just focusing on the target disease. To do this, it is necessary to deepen our understanding of the pathology of arteriosclerosis as well." (Professor Kono)
Research is beginning to elucidate the mechanisms by which uric acid and cholesterol crystals are involved in chronic inflammation, and some have been found to be effective in suppressing the progression of arteriosclerosis. However, these results are still limited to the mouse level. "There are still many hurdles to overcome before we can apply this to clinical practice, but we hope that our research will serve as the starting point for new treatment strategies," says Professor Kono.
While a clinician's treatment is an act of saving the patient in front of them, basic research leads to saving patients in the future. Driven by the desire to save as many people as possible from chronic inflammatory diseases, Professor Kono is devoting himself to both his clinical work and research.