トピックス
- 教育・研究
2025年08月27日
- プレスリリース
濱准教授・横山教授らの参画する研究グループが、トランス脂肪酸が老化・炎症を促進する分子メカニズムを発見しました板橋キャンパス
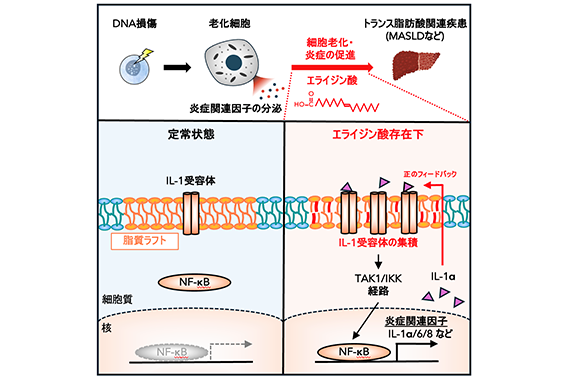
2025年8月5日(火)、帝京大学薬学部准教授 濱弘太郎と同教授 横山和明は、東北大学大学院薬学研究科大学院生 小島諒太氏、同研究科准教授 平田祐介氏、同研究科教授 松沢厚氏らの研究グループとの共同研究において、最も主要なトランス脂肪酸であるエライジン酸が、DNA損傷の際に起きる細胞老化および炎症を促進することを発見しました。
一部の加工食品に含まれるエライジン酸などのトランス脂肪酸の摂取は、過去の疫学的知見から、動脈硬化症や生活習慣病(MASLDなど)をはじめとした加齢や炎症が関連する疾患のリスク因子とされてきましたが、炎症誘導の詳細な分子機構は不明でした。
本研究にて、エライジン酸は細胞膜上の脂質ラフトと呼ばれる膜上の微少領域に取り込まれ、この領域内にサイトカインIL-1受容体を集積させることで、受容体下流における炎症誘導シグナルの活性化を増強し、細胞老化や炎症反応を増幅することが明らかになりました。エライジン酸を摂取させたマウスでは、心血管疾患や肝がんの引き金となるMASLDの発症時に、肝臓の細胞老化および炎症が亢進しました。動脈硬化症やMASLDなどのトランス脂肪酸関連疾患の、画期的な予防・治療戦略の開発につながることが期待されます。
本成果は、8月5日(火)に国際科学誌iScienceにオンライン掲載されました。
プレスリリースはこちら
掲載論文はこちら
濱准教授についてこちら
横山教授についてはちら
Teikyo lab.についてはこちら